All too often, individuals in the midst of chronic, distressing symptoms are passed from one specialist to the next because their standard blood work, x-rays, and other diagnostic tests score in the “normal” range. This is incredibly frustrating, as it can be more challenging to cope with illness or discomfort when the medical tests report “healthy” results. When this happens, people often find relief from seeking help from a doctor of naturopathic medicine. This is because naturopathic, functional medicine doctors investigate the unique chemical makeup of each person in order to discover the underlying causes of disease.
One method they use to find the root problem is by ordering some lesser known, but highly effective, lab tests. There are nine essential blood tests you need to know about, because they could literally save your life. Even though these tests aren’t always part of the “brick and mortar” of doctor-ordered lab tests, they are paramount in detecting risk factors for life threatening diseases. When you have identified your own unique risks, you are empowered to make the necessary lifestyle changes to prevent the onset of these diseases.
ASK YOUR ND TO RUN THESE ESSENTIAL LAB TESTS
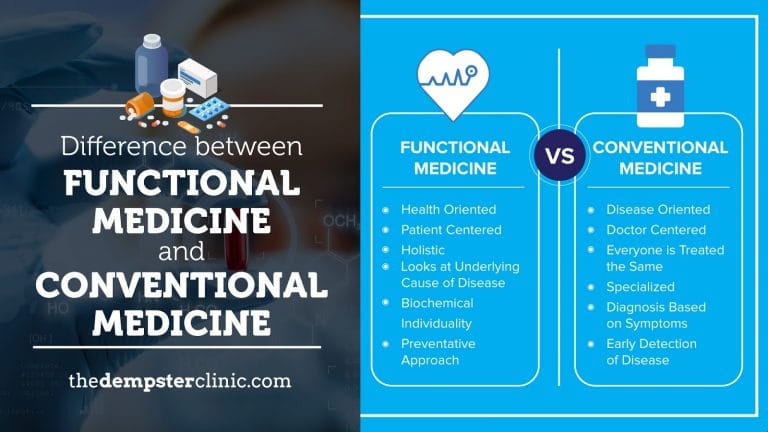
Are you tired of not receiving the care you deserve? Unlike functional medicine doctors, many doctors who follow a conventional medicine approach focus on diagnosis-based symptoms and early detection of disease. Instead of waiting for the signs of a disease to emerge, ask your doctor about the following nine lab tests. Their results can reveal your risk levels, enabling you to modify your lifestyle and prevent a life-threatening disease from emerging.
1. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (Hs-CRP) Test
The C-reactive protein is a type of protein that multiplies in your body as inflammation levels increase. A standard test is the C-reactive Protein (CRP) test, which calculates the overall levels of inflammation within your body, especially those affecting the cardiovascular system. Doctors typically use this test to look for signs of infections and other medical conditions. The problem with a CRP test alone is that it is not as sensitive an indicator as a High Sensitivity C-reactive Protein test (Hs-CRP).
Whereas a CRP test detects elevated levels of this protein, an Hs-CRP measures low levels of the C-reactive protein. There is a strong correlation between a high Hs-CRP score and an increased risk for heart attacks. This test is useful for assessing how likely you are to develop coronary artery disease, which is a narrowing or clogging of the arteries due to plaque buildup. It also helps predict the risk of stroke and heart disease in individuals who have not developed heart disease already.
Additionally, the Hs-CRP test is useful in forecasting how a person with heart disease will respond to treatment and what their recovery will look like. Taking this lab test can help prevent heart disease or a stroke by showing that an individual is at risk and should begin preventive measures.
This is a critical screening for anyone with high risk factors for heart disease or with a family history of heart disease. The healthy range is 1.0mg/mL or less.
2. Homocysteine Test
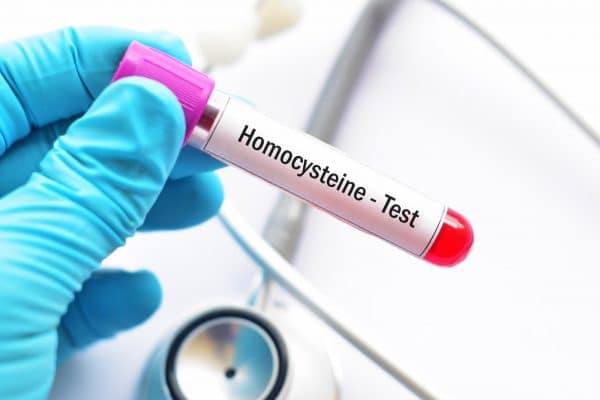
Your body uses homocysteine to build protein and create and maintain tissue. While necessary in certain amounts, excess homocysteine, also referred to as hyperhomocysteinemia, may increase your risk of stroke, various types of heart disease, and peripheral artery disease. Since hyperhomocysteinemia typically has no symptoms of its own, deficiencies in vitamin B12 or folate are often the first indicators that a homocysteine test should be run.
This is an important blood test to run in order to make sure that your arteries are strong and healthy. In addition, it is also a good indicator of the methylation pathways in your body. Methylation is required for preventing the expression of certain inherited genes that may predispose you to life-threatening diseases. For example, methylation may inhibit the expression of a gene in your DNA that, if expressed, would cause breast cancer. The optimal range for homocysteine is 6.0umol/L or less.
3. Lipoprotein A Test
A conventional cholesterol blood test measures your total cholesterol, which is comprised of high density lipid protein (HDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglycerides. In contrast, an LP(a) test analyzes Lipoprotein-A, a specific type of LDL cholesterol that can triple heart disease risk. The LP(a) test is important for detecting overall levels of LP(a), as well as measuring particle size.
Size is important because the size of these fatty particles dictates how they behave. Higher levels of large particles are less risky, while smaller particles pose more of a threat. Larger particles move more easily through the body, as they have a tendency to bounce off artery walls. Smaller particles, on the other hand, are more dense and can penetrate the artery lining, collecting into clumps of plaque that can ultimately lead to coronary heart disease.
It is important to detect high levels of LP(a) as early as possible, as elevated levels reduce your body’s natural defenses against clotting, ultimately leading to dangerous blockages. This is because the more Lp(a) you have, the stickier these LDL particles become. As a result, they cling even more stubbornly to the lining of blood vessels. Healthy values for an LP(a) test should be less than 20 mg/dl.
4. Fibrinogen Test
One of the proteins in your body that helps form blood clots is called fibrinogen. This is a necessary substance, in healthy amounts. However, excess fibrinogen is cause for concern. Too much of this protein may create blood clots in the arteries, potentially causing a stroke or heart attack.
A surplus of fibrinogen can indicate that you already have or are at risk for developing atherosclerosis (coronary heart disease). Additionally, too much of this protein can exacerbate existing injury to the artery walls.
In addition, fibrinogen is another marker for inflammation. Chronic inflammation disrupts your immune system’s natural functioning and is a major cause of diseases like diabetes and Alzeimer’s.
If you have an increased risk of heart disease or a family history of heart disease, make it a priority to have your fibrinogen levels tested. Generally speaking, a normal fibrinogen level is between 200 and 400 mg/L.
Keep in mind that lifestyle choices affect your fibrinogen levels. Smoking, living a sedentary lifestyle, drinking excessively, and taking supplemental estrogen — whether from birth control pills or hormone therapy — are all risk factors for increasing fibrinogen beyond the healthy range.
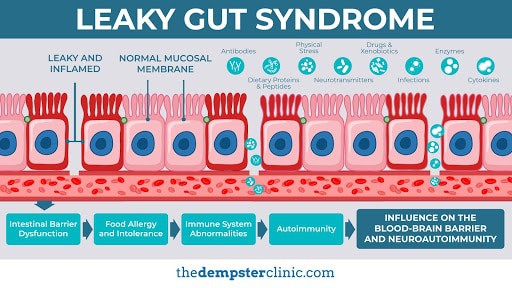
5. Zonulin Test
Your gut wall consists of epithelial cells. These epithelial cells are attached to each other by “tight junctions,” or protein complexes. Zonulin is a type of protein that regulates tight junction. When your gut is unhealthy, the epithelial cells release zonulin, which can cause the the tight junctions to disassemble. Notably, wheat contains gliadin, a type of protein that may trigger the body to release more zonulin. Unsurprisingly, zonulin levels are especially elevated in individuals with celiac disease.
Too much zonulin is linked to polycystic ovary syndrome, depression, autism, and Type 1 and 2 diabetes, amongst many other conditions. Excess zonulin may also indicate the presence of Leaky Gut Syndrome, which is also referred to as intestinal permeability. Leaky Gut Syndrome can leave you vulnerable to a host of chronic health problems, many of which are life threatening.
6. HbA1c Test
Are you interested in aging well and decreasing your risk of chronic disease? Do you have diabetes? If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, make sure to have your doctor run an HbA1c test. HbA1c refers to glycated hemoglobin. Hemoglobin, a protein that helps move oxygen throughout your body, becomes “glycated” when it fuses with the glucose in your bloodstream.
The ideal values for HbA1c are 3.5 – 5.5%. Heightened HbA1c levels can reveal that your body has had a long-term inability to handle sugars, which is essentially the “caramelizing” of your inner organs and tissue. This is an extremely important test because high values indicate that you may have five times more than the average person’s risk for heart disease! They also show that you are more likely to experience diabetic complications.
7. Fasting Insulin Test
Serious medical conditions like obesity, metabolic syndrome, hypoglycemia, and diabetes aren’t like the common cold; they don’t develop over the course of a day or two. Again, this is why it can truly change your life to have important blood tests done to predict your risk before a dangerous condition manifests completely.
The Fasting Insulin Test shows how well your body maintains blood sugar levels, which is incredibly important for a number of factors. Persistently elevated insulin levels worsen inflammatory processes in the body, creating higher risks for developing Type 2 Diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. The optimal range should be less than 8.4 uIU/ml.
The Fasting Insulin Test also detects insulin resistance, a crucial element of Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. This test is unique because your insulin levels tend to become dysregulated before HbA1c or glucose levels, so it helps you detect your risk for diabetes and other serious conditions earlier than HbA1c or glucose tests.
Type 2 Diabetes is preventable, and catching the early warning signs are key. If the test reveals that you are at risk for developing diabetes, talk to your doctor about preventive measures such as exercise, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and keeping your blood pressure under control.

A final note on the Fasting Insulin Test: if you’re looking to boost your metabolism, it is essential to have a detailed understanding of your hormones prior to beginning a treatment program. One of the most important tests for gaining this understanding is the Fasting Insulin Test.
8. 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D (25)
Vitamin D is an essential vitamin for many reasons! It’s essential for regulating mood and maintaining bone health. Additionally, a deficiency in Vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Like most nutrients, Vitamin D goes through multiple processes before your body actually uses it. When it goes through your liver, it is converted to calcidiol, a chemical also referred to as 25-hydroxyvitamin D. This chemical is what the 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D test measures.
The unit of measurement used for the 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D test is either nanomoles/liter (nmol/L) or nanograms/milliliter (ng/mL). Less than 12ng/mL, or 30 nmo/L, indicates a deficiency. Levels above 125 nmol/L (50 ng/mL) are considered above the normal healthy range.
This is a useful test primarily because too much or too little of this vitamin may indicate poor bone health. If you have this test done early enough, you may be able to prevent the onset of osteoporosis.
This is also a helpful test for individuals suffering from depression; research has shown that Vitamin D supplements can alleviate symptoms of depression in people who are deficient in the vitamin. You can also get this essential nutrient from foods like eggs, fish, and dark leafy greens. Sunlight is another great natural source of Vitamin D!

9. Cholesterol/HDL Ratio Test
Contrary to popular belief, not all cholesterol is bad. In fact, this fatty substance is an instrumental part of building new tissue, aiding hormone function, assisting the digestive process, and safeguarding your nerves. HDL is the “good” type of cholesterol, and it helps remove LDL from your bloodstream by delivering it to your liver. As discussed in the Lipoprotein-A Test description, LDL cholesterol is dangerous because too much of it greatly increases your likelihood of developing heart disease.

As you can see, it is advantageous to have higher levels of HDL and lower levels of LDL in your bloodstream. Testing your Cholesterol/HDL ratio can expose great risk for heart disease, and knowing if you’re in an unhealthy range indicates that you need to start making heart-healthy lifestyle changes. Your cholesterol ratio is determined by dividing your total cholesterol by your HDL. The ideal ratio is 3.5 and should be no higher than 5, according to the American Heart Association.
FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE TESTS AND DIAGNOSTICS AT THE DEMPSTER CLINIC- CENTER FOR FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE
Understanding each of these blood tests can be confusing, and knowing what to do with the results can be even more challenging. However, I can work with you to understand these tests and develop a specific health plan tailored to your individual needs. The Dempster Clinic- Center for Functional Medicine provides state-of-the-art tests and diagnostics, collaborating with a number of world leading laboratories to ensure the availability of a wide range of quality lab testing.
Please take the opportunity to schedule a Complimentary 15-minute Discovery Session with me, which can take place over the phone or at the clinic. It gives you an opportunity to learn more about the services I offer, with no strings attached.
Please schedule an appointment today! Your best health awaits you.
Dr. John Dempster BSc., ND, FAAFM
The Dempster Clinic- Center for Functional Medicine